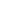What is nickel-based tungsten carbide?
Nickel-based tungsten carbide is a composite material composed of a nickel-based self-fluxing alloy (such as Ni60) as a bonding phase and tungsten carbide (WC) hard particles. It is characterized by the toughness and self-fluxing properties of nickel-based alloys and the high wear resistance of tungsten carbide.
- Material composition
Nickel-based alloy (such as Ni60): As a bonding phase, it provides corrosion resistance and high temperature performance.
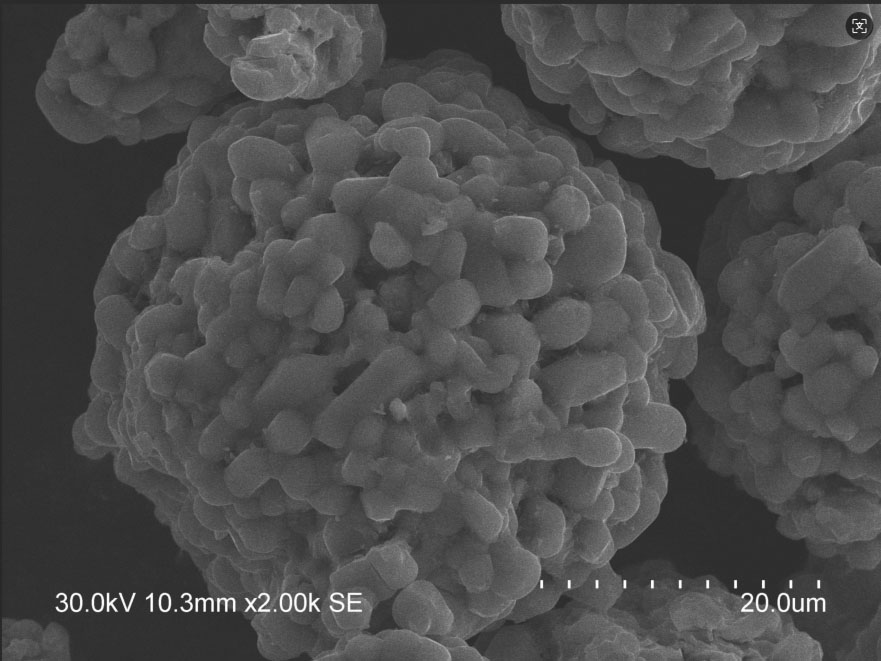
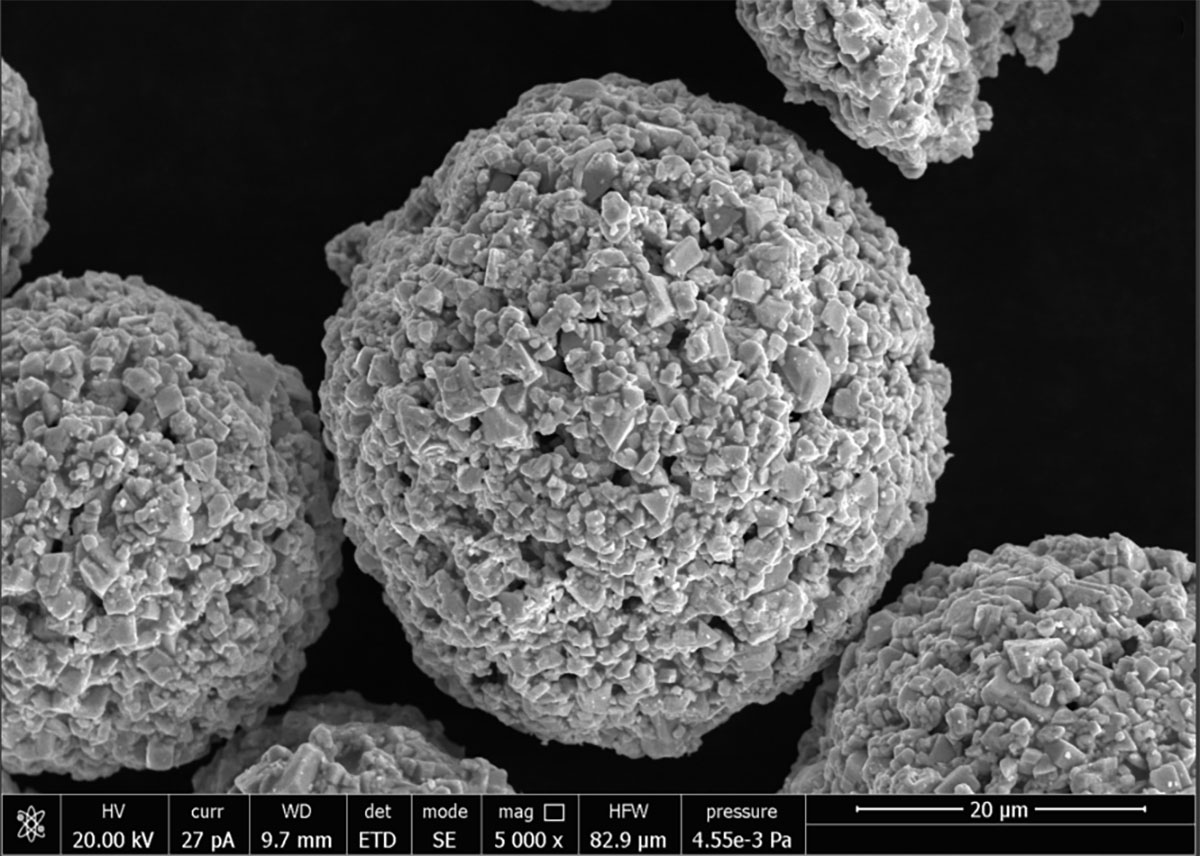
Tungsten carbide (WC): Hardness ≥ HV2000, usually accounting for 30%-60% (adjusted according to wear resistance requirements).
- Core characteristics
Ultra-high wear resistance: WC particles significantly improve the ability to resist abrasive wear, and the wear resistance is 3-5 times higher than that of pure nickel-based alloys.
High temperature resistance: Nickel-based alloys remain stable below 600°C, and WC is not easily oxidized at high temperatures (better than chromium carbide).
Good toughness: nickel matrix buffers impact and prevents WC particles from peeling off.
- Typical applications
Mining machinery: crusher roller surface, excavator tooth tip.
Oil drilling: drill collar, stabilizer.
Metallurgical industry: rolling mill guide plate, feed roller.
Agricultural machinery: rotary tiller, harvester blade.
Preparation process points
- Mixing method:
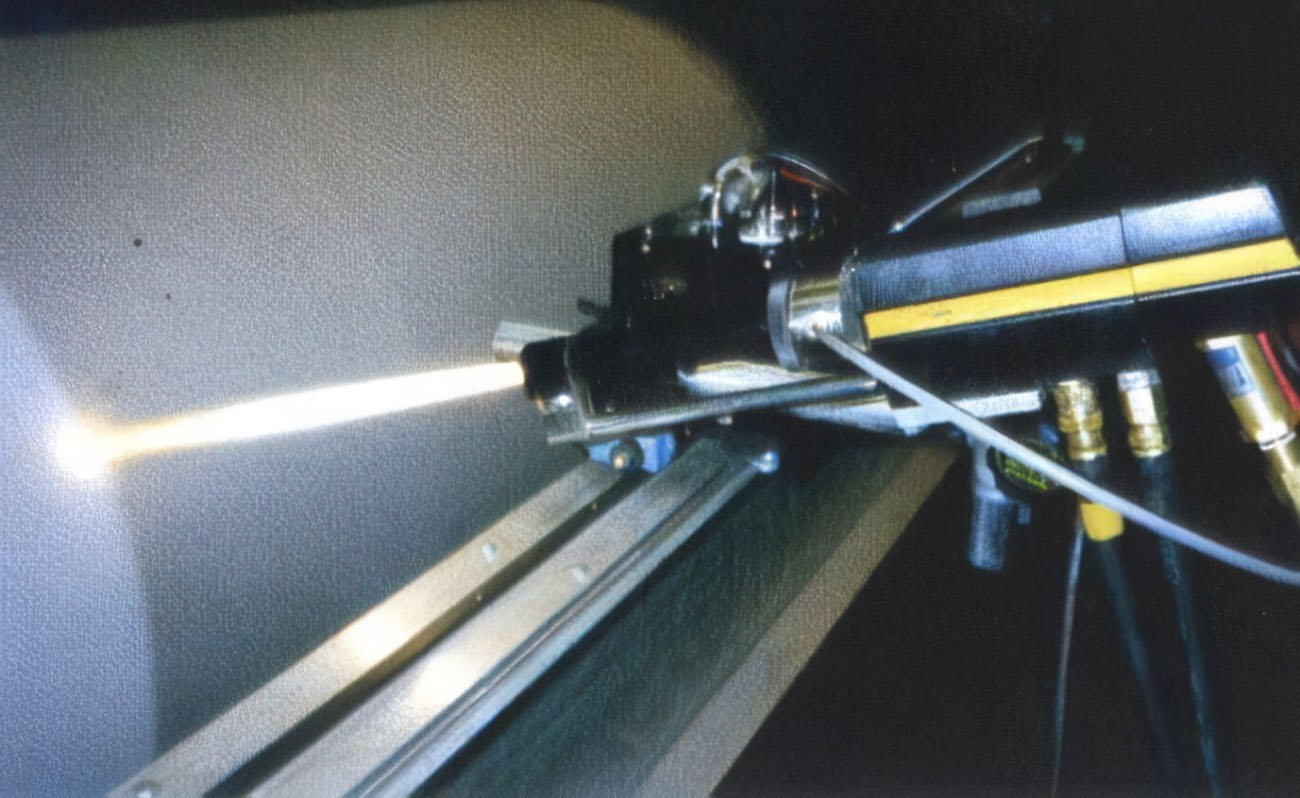
Mechanical mixing: nickel-based powder and WC powder are directly mixed (low cost, but WC is unevenly distributed).
Coated powder: WC particle surface is pre-plated with nickel to improve the bonding strength with the matrix (excellent performance, high price).
- Common processing technology:
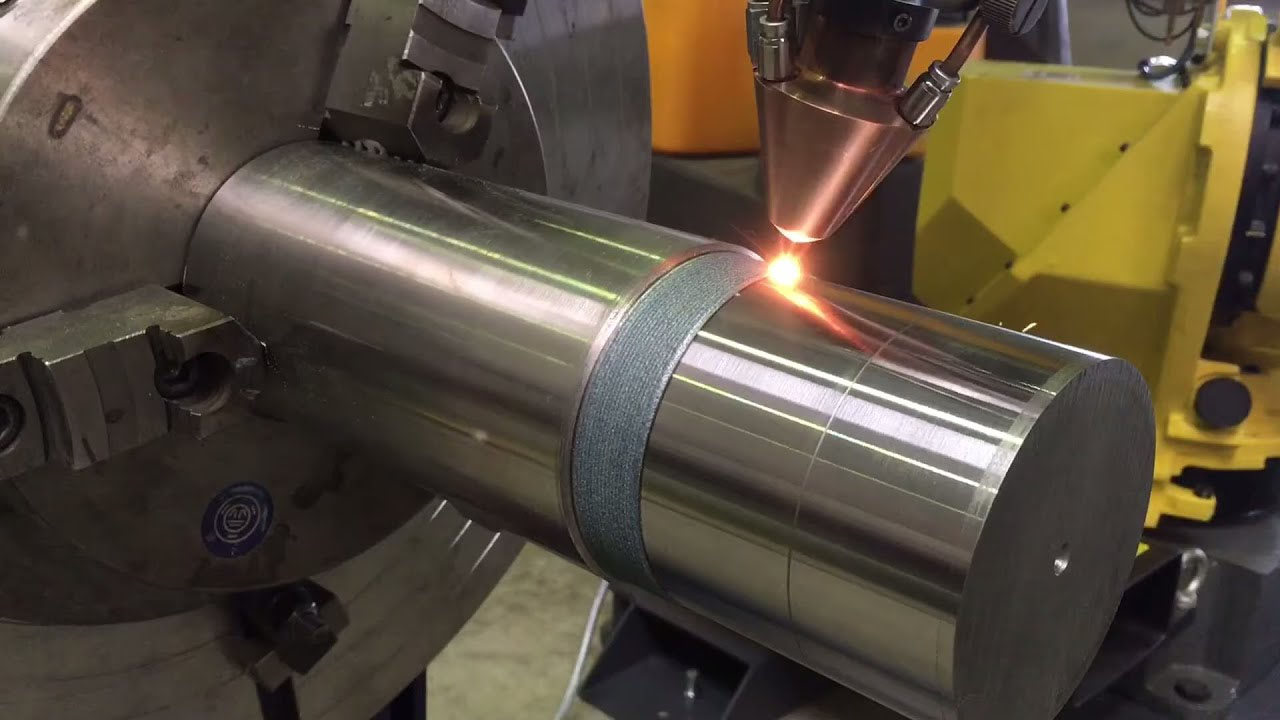
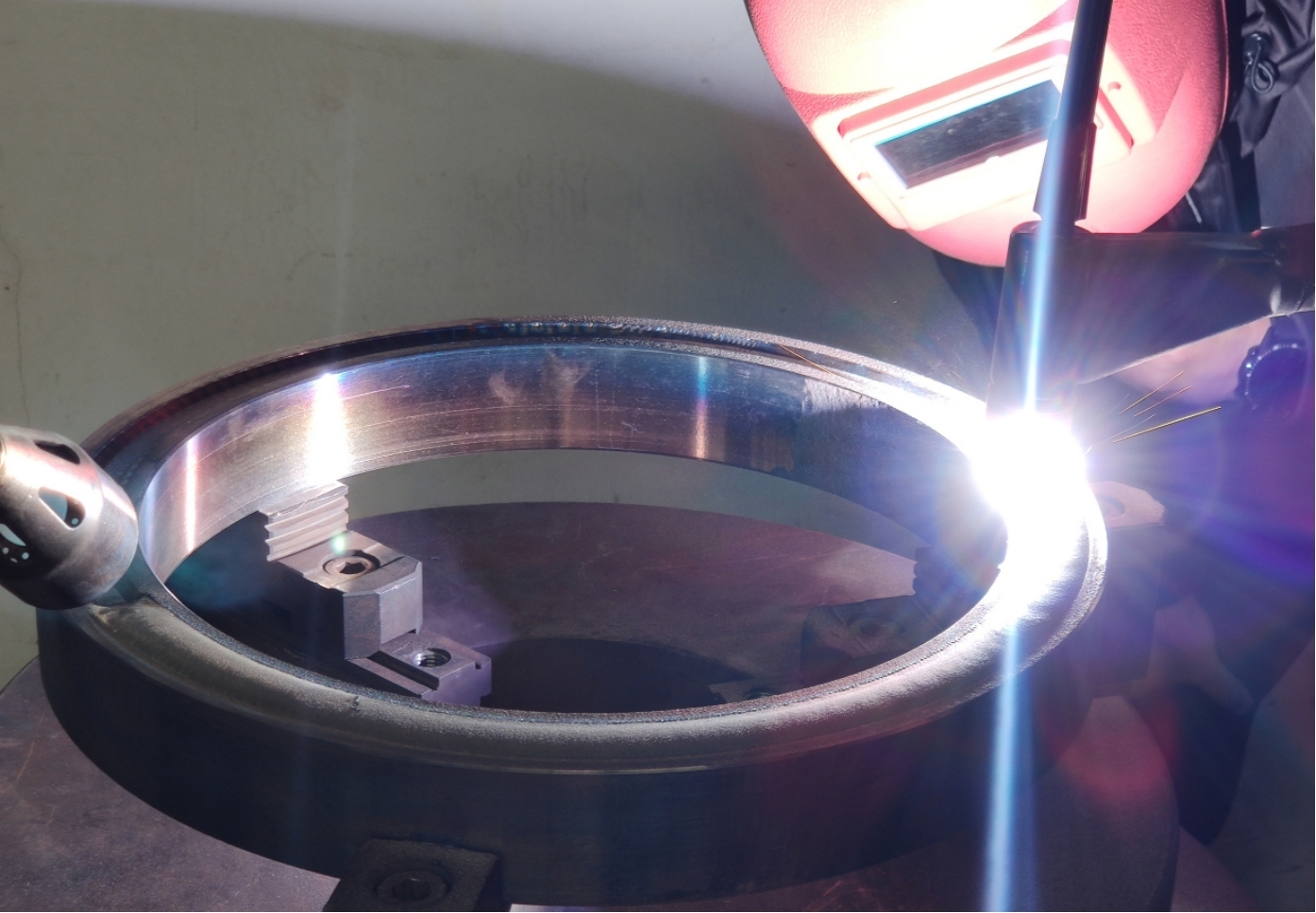
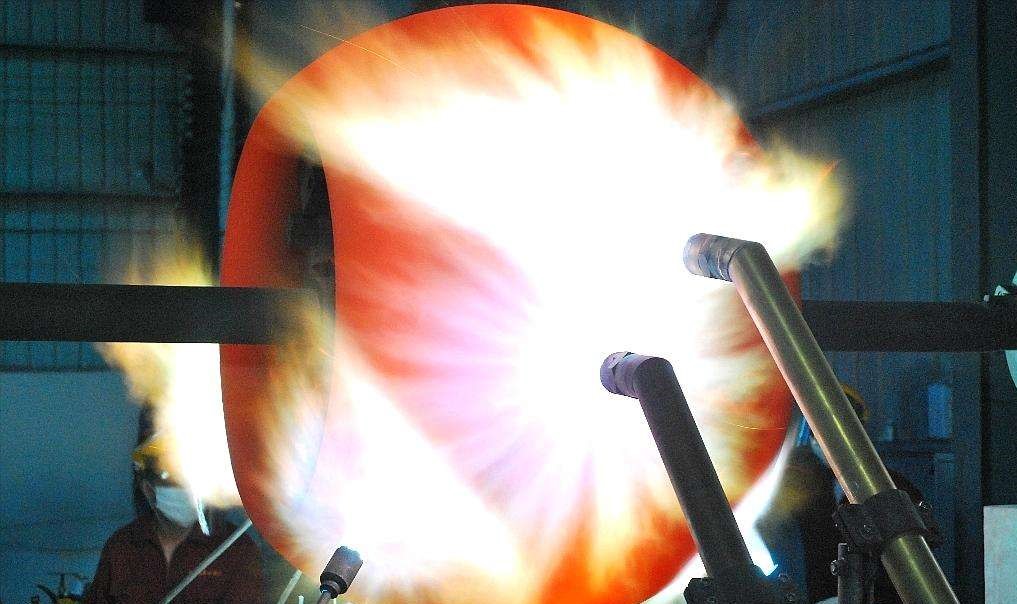
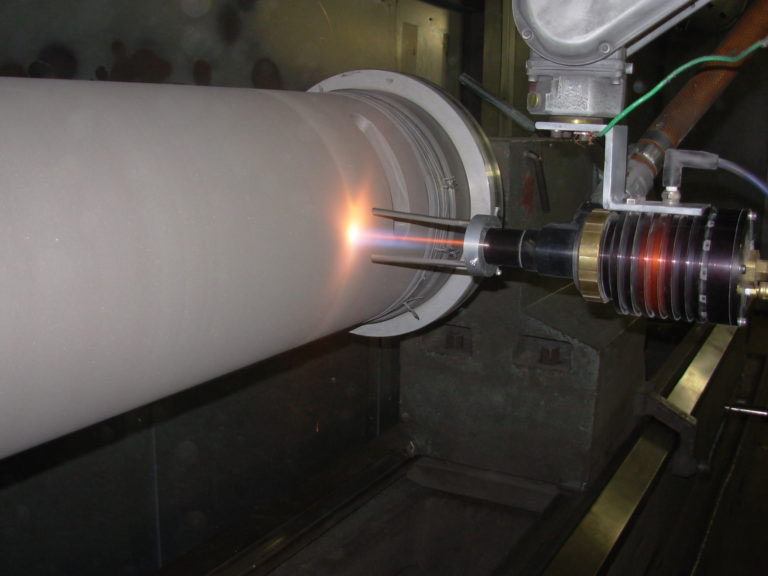
Oxyacetylene spray welding: suitable for on-site maintenance, but the flame temperature needs to be controlled (to avoid WC decomposition into W2C).
Plasma surfacing/laser cladding: concentrated energy, less WC decomposition, suitable for high-precision parts.
- Notes:
Upper limit of WC content: more than 60% will easily lead to increased brittleness of the coating.
Process matching: high-temperature processes (such as plasma) require coarse-grained WC (to avoid complete melting).
Nickel-based tungsten carbide composite materials are ideal for extreme wear conditions, especially for scenarios that require both impact resistance and wear resistance.