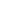Powder Tungsten has emerged as a cornerstone in various modern industries. Its unique properties make it invaluable in manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics. This material demonstrates exceptional hardness and high melting point. Such features enable it to perform under extreme conditions.
In the realm of aerospace, Powder Tungsten is often used in components that require durability. The ability to withstand high temperatures is crucial for aircraft engines. Similarly, in electronics, it serves as a vital element in producing filaments and contacts. It ensures reliable performance in devices we use daily.
However, relying heavily on Powder Tungsten raises questions. What if the supply chain faces disruptions? The mining process can also have environmental impacts. Industries must balance practicality with sustainability. As technology advances, finding alternatives may become necessary. This reflects an ongoing challenge as industries strive for innovation while ensuring responsible resource use.

Powder tungsten is a remarkable material in modern industries. Its high melting point is one of the most significant features. This makes it suitable for extreme conditions. Industries require materials that perform well under heat. Powder tungsten fits this need perfectly.
The density of tungsten is impressive too. It is heavy, providing stability in various applications. Tools made from powder tungsten have durability. They withstand wear and tear better than many alternatives. However, working with this material can be challenging. The fine particles can create safety concerns. Proper handling is essential to avoid health risks.
Tungsten also has unique electrical properties. Its ability to conduct electricity is beneficial in various electronic applications. These aspects make it a favorite among engineers. Yet, the cost of powder tungsten can be high. This leads to ongoing discussions about its efficiency and usage. Industries continuously explore ways to optimize its application.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Density | 19.3 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 3422 °C |
| Hardness | 7.5 - 8.0 Mohs scale |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good conductor |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity ~ 165 W/(m·K) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion |
| Applications | Used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and military sectors |
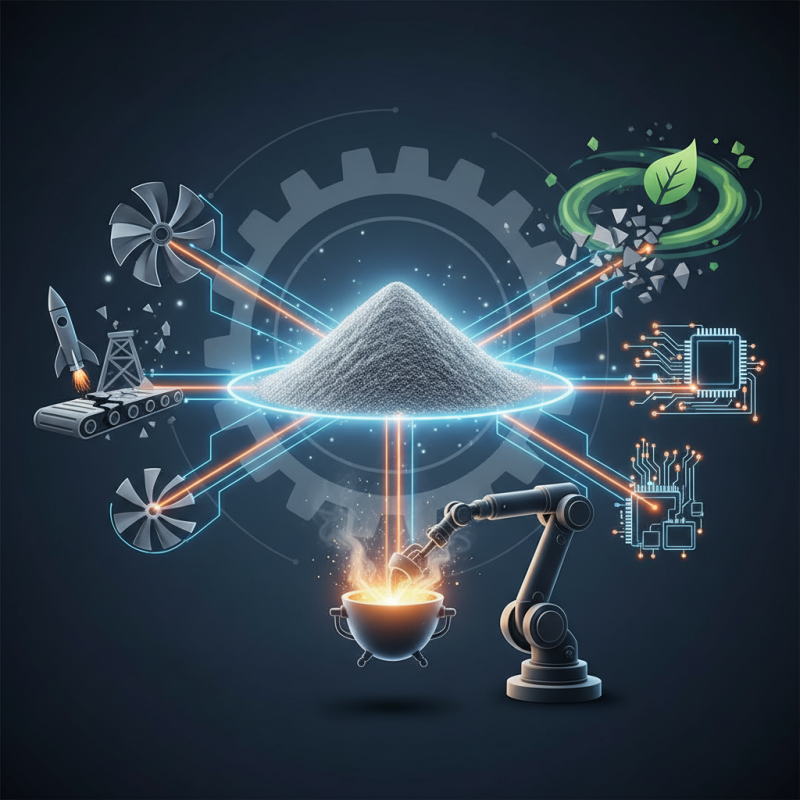
The use of powder tungsten has a rich history in various industries. Initially identified for its high melting point and density, tungsten became essential in the production of hard metals, cutting tools, and electrical contacts. In the 20th century, advancements in powder metallurgy paved the way for greater applications of tungsten. Reports indicate that global tungsten consumption has increased by over 5% annually, primarily driven by the demand in manufacturing sectors.
Tungsten powder plays a pivotal role in industries such as aerospace and automotive. Its unique properties ensure durability and performance under extreme conditions. Powder tungsten is often used in engine components and cutting tools, supporting efficiency and longevity. Data from industry analyses suggest that over 30% of tungsten is utilized in these fields alone.
Tips: Consider exploring recycling options for tungsten. It can help reduce waste while ensuring a steady supply. Additionally, while tungsten is highly regarded, sourcing and processing can lead to environmental concerns. Reflecting on the sustainability of tungsten production is vital. Understanding these issues can drive better industry practices.
Powder tungsten plays a crucial role in high-temperature environments. Its remarkable melting point, over 3,400 degrees Celsius, makes it ideal for extreme conditions. Industries like aerospace and defense rely on this metal for various applications. It maintains strength and stability when exposed to intense heat.
In manufacturing, powder tungsten is used for producing components that endure high thermal stresses. For example, gas turbine engines often incorporate tungsten parts. These parts must withstand not only heat but also mechanical fatigue. However, some processes can leave room for improvement. Powder handling requires careful attention to minimize contamination. Impurities in the powder can lead to failure in critical components.
Tungsten also finds its place in electrical applications like electrodes in arc-welding. At elevated temperatures, its performance remains consistent. Yet, the cost of raw tungsten can be a barrier. Balancing quality and expense is a challenge for many manufacturers. They must continually seek new methods for efficiency. The pursuit of innovation remains essential in using powder tungsten effectively in high-temperature settings.
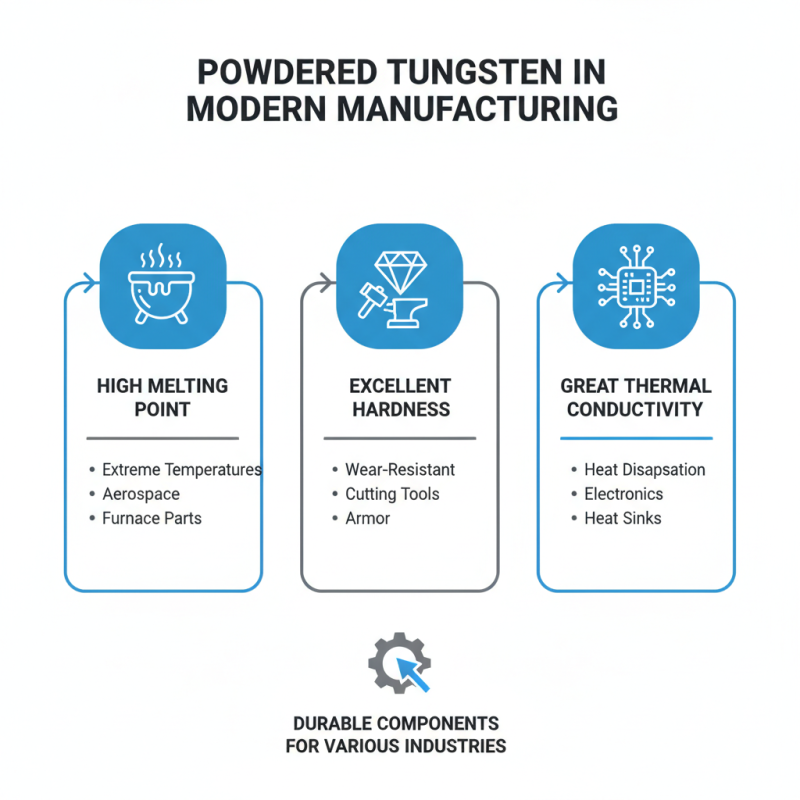
Powder tungsten plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing. Its unique properties bring many advantages to various industries. This material has a high melting point, excellent hardness, and great thermal conductivity. These features make it ideal for creating durable components.
The economic impact of powder tungsten is significant. It enhances production efficiency and reduces costs. Industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics rely on tungsten’s performance. Parts made from powder tungsten often last longer, saving money on replacements. For manufacturers, this means lower operational costs and increased profitability.
Tips: Consider using powder tungsten in applications where durability is key. Evaluate your production processes to see how this material can enhance efficiency. Investing in quality materials can yield great returns. Always stay informed about market trends and price fluctuations.
The demand for powder tungsten is rising, driven by its unique properties. Industries rely on it for applications like electronics and aerospace. However, several challenges impact its efficiency. For instance, the production process can lead to inconsistencies in particle size. This can affect performance in high-precision applications.
Recent reports indicate that powder tungsten production faced a 15% decline due to raw material shortages. Such fluctuations can hinder supply chains, raising costs for manufacturers. Additionally, environmental concerns about extraction methods have surfaced. Many companies are now reconsidering their sourcing strategies to align with sustainable practices.
Future trends suggest a shift towards recycling tungsten materials. The world generated over 100,000 metric tons of tungsten in 2022, and nearly 30% remains untapped in discarded products. Transitioning to a circular economy for tungsten could mitigate supply challenges. However, the technical hurdles in reclaiming and processing recycled tungsten remain significant. Reflections on these issues highlight the complexities in adapting to industry demands while maintaining sustainability.