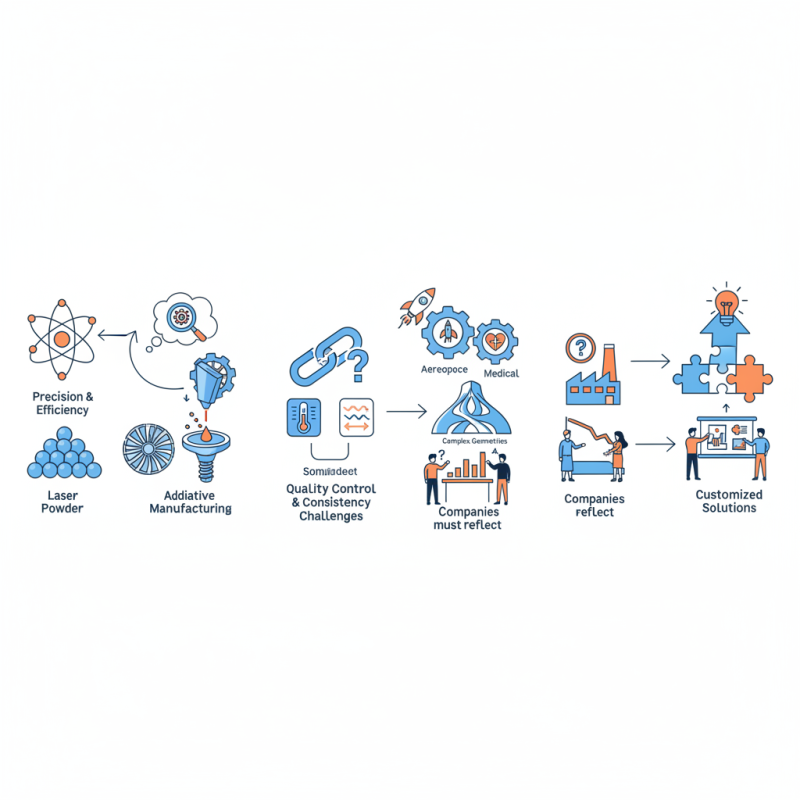
In recent years, the manufacturing industry has increasingly turned to Laser Powder as a solution for various applications. Experts in the field, like Dr. Emily Carter, have noted, “Laser Powder will redefine how we approach precision and efficiency in production.” This statement highlights the significant potential of Laser Powder in revolutionizing traditional manufacturing processes.
Laser Powder, a vital component in additive manufacturing, offers versatility. It allows for building complex geometries that were once difficult or impossible to achieve. Industries such as aerospace and medical are particularly excited about these advancements. They are exploring new designs and materials, pushing the boundaries of what can be created. However, challenges remain. Quality control and consistency in Laser Powder production need further improvement. Companies must reflect on these issues to maximize the benefits of this technology.
As the demand for customized solutions grows, the role of Laser Powder becomes even more crucial. Manufacturers face the task of adapting to these changes while ensuring reliability. The journey ahead may be complex, but the possibilities with Laser Powder are immense, inspiring ongoing exploration and innovation.
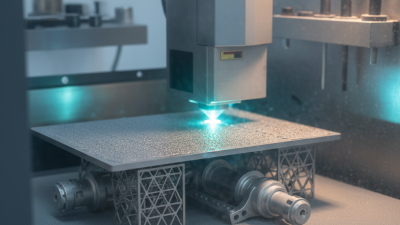
Laser powder technology has transformed manufacturing processes. This technology involves the precise use of powdered materials, which are melted and fused with lasers. It enables the creation of complex shapes that traditional methods struggle with. The ability to layer materials allows for unique designs and improved structural integrity in products.
Using laser powder for manufacturing can minimize waste. However, controlling the powder quality is challenging. Variations in grain size can affect the final product’s strength and durability. It’s essential to maintain consistency in powder composition during production.
Tips: Always check the calibration of laser equipment. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance. Take time to evaluate the end products critically; imperfections may reveal areas for improvement. Being attentive to these factors enhances overall quality.
Laser powders are integral to advanced manufacturing. Their types and properties significantly affect the performance and quality of end products. Common types include stainless steel, titanium, and cobalt chrome powders. Each has unique attributes that cater to various applications.
Stainless steel powders exhibit good corrosion resistance and strength. According to industry reports, they account for nearly 30% of metal powder sales. Their versatility makes them popular in aerospace and automotive sectors.
Titanium powders are lightweight yet strong, widely used in medical implants. Interestingly, they can be quite expensive, leading to concerns over cost efficiency.
Cobalt chrome powders are known for high wear and corrosion resistance. Reports suggest they enhance longevity in harsh environments. However, the production process can generate inconsistencies in particle size, which affects workability. This highlights the ongoing challenges in standardizing powder quality across various manufacturers.
Laser powder has gained significant attention in manufacturing processes. It plays a crucial role in additive manufacturing and traditional methods. The use of laser powder enables the creation of complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with conventional techniques. This opens up new possibilities for innovation.
One of the key processes involving laser powder is selective laser melting (SLM). In this technique, a laser selectively melts powder layers, fusing them together to form solid parts. It requires precision and a deep understanding of material properties. Even small errors can lead to defects. For instance, incomplete melting might weaken the final product. Another method, laser cladding, involves adding powder to an existing component. It enhances surface properties but can sometimes lead to undesirable residual stresses.
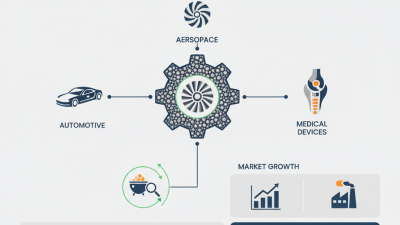
The versatility of laser powder applications extends to aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. These sectors benefit from lightweight components and tailored material properties. However, challenges remain, such as ensuring consistent powder quality and managing thermal effects. The technology still needs refinement and understanding, emphasizing the importance of continuous research and development.
Laser powder plays a pivotal role across various manufacturing industries. In aerospace, its precision enhances component durability. For example, using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), companies can reduce weight by up to 70% while maintaining structural integrity. This process allows the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve.
In the medical field, laser powder applications are revolutionizing the production of implants. Customization is key here. Implants can be tailored to individual patient needs, improving recovery times. Data indicates a 30% increase in the efficiency of implant designs using additive manufacturing techniques with laser powders.
The automotive industry also benefits greatly. Laser powder enables rapid prototyping and production of parts with intricate designs, reducing lead times. Reports suggest that the time for producing prototypes can be cut by 50%. However, challenges remain, such as the need for quality control protocols to ensure consistency. As technologies evolve, the search for flawless production continues.
Laser powder technology is evolving rapidly. New advancements improve its applications in manufacturing. One area of focus is enhancing powder quality. High-quality powders lead to better end products.
Innovations in laser powder delivery systems are also emerging. These systems aim for better precision and efficiency. Some systems might still face challenges in reducing waste. However, they show promise for faster production rates. Manufacturers are looking into automation to streamline processes further.
Environmentally friendly practices are becoming more prevalent. Companies are exploring ways to recycle laser powder effectively. This can reduce costs and environmental impact. While challenges remain, the push for sustainability is strong. The future of laser powder technology looks bright, with many changes on the horizon.