High Melting Point Alloys are essential in various industries. These alloys are designed to withstand extreme temperatures. They play a significant role in aerospace, automotive, and even energy sectors. The unique properties of High Melting Point Alloys make them suitable for applications that require durability and resistance to heat.
Their impressive melting points allow for use in harsh environments. Engineers rely on these materials for components that operate under significant stress. However, working with High Melting Point Alloys poses its own challenges. The manufacturing process can be complex and costly. This complexity leads to questions about their practicality and efficiency.
Understanding High Melting Point Alloys is crucial for innovation. They hold the potential to enhance performance and safety in critical applications. Yet, it is important to consider their limitations. The balance between performance and cost often demands careful evaluation. This exploration will delve deeper into the fascinating world of High Melting Point Alloys.


High melting point alloys are critical in many industrial applications. These materials excel in environments with extreme temperatures. For instance, nickel-based superalloys can withstand temperatures up to 1,600°C. This ability makes them ideal for aerospace and turbine engines. Their alloying elements typically include tungsten, rhenium, and molybdenum. These elements contribute to their impressive heat resistance.
Understanding these alloys requires knowledge of their properties. They are often characterized by their strength and durability at high temperatures. According to recent industry reports, high melting point alloys account for a growing segment of the materials market, projected to reach USD 7 billion by 2025. Their properties make them valuable, but they are also challenging to process. This complexity can lead to increased costs and longer production times.
Tips: When selecting a high melting point alloy, consider the specific application requirements. Look for compatibility with other materials and processing methods. Researching supplier options is also crucial in ensuring quality. Even minor processing errors can lead to significant performance issues. Balancing cost and performance needs is vital in making these choices.
High melting point alloys are fascinating materials. They are known for their exceptional thermal stability. These alloys maintain their properties even at elevated temperatures. They're often used in applications like aerospace and nuclear reactors.
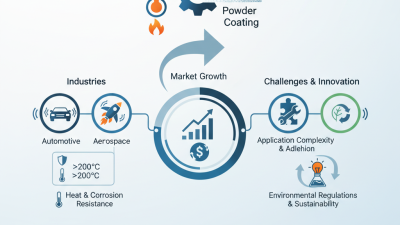
One key characteristic of these alloys is their resistance to thermal degradation. This means they can endure extreme heat without losing strength. Additionally, they exhibit low expansion rates. This property is essential in precision engineering. High melting point alloys can also withstand oxidation. This makes them ideal for harsh environments.
**Tips:** When working with these materials, always consider the manufacturing processes. Post-processing can enhance their properties. Also, remember that not all high melting point alloys are created equal. Testing is crucial to ensure they meet specific requirements. Balancing performance and cost is sometimes challenging. Adjustments in composition might lead to better results.
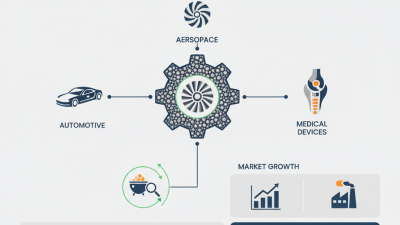
High melting point alloys are crucial in various high-temperature environments. One major application is in the aerospace industry. Here, components must withstand extreme conditions. For instance, turbine blades often reach temperatures near 1,500°C. Alloys like nickel-based ones offer durability and heat resistance. These materials help improve efficiency and reduce emissions in engines.
Another significant use is in the automotive sector. High-performance vehicles utilize these alloys for engine components and exhaust systems. A study from the International Journal of Automotive Engineering notes that high melting point alloys can enhance performance by up to 15%. However, the manufacturing process can be complex. It often requires precise control over temperature and cooling rates, leading to potential quality issues.
In electronics, these alloys see growing interest due to their thermal stability. High melting point alloys are used in heat sinks and connectors. The demand for reliable materials in electronics continues to rise. However, sourcing raw materials can be challenging and costly. As industries advance, the need for innovation in high melting point alloy production is apparent. New methods are required for sustainability and efficiency.
| Alloy Type | Melting Point (°C) | Common Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Alloy | 3422 | Aerospace, Military, Medical Devices | High density, Excellent electrical conductivity |
| Molybdenum Alloy | 2620 | High-temperature applications, Electrical contacts | Good strength at high temperatures, Corrosion resistant |
| Tantalum Alloy | 2980 | Chemical processing, Medical implants | Excellent corrosion resistance, Biocompatibility |
| Rhenium Alloy | 3186 | Aerospace engines, Gas turbine components | Superior high-temperature strength, Ductility |
| Chromium Alloy | 1907 | Tooling, Coatings | High hardness, Wear resistance |
High melting point alloys are critical in many industries. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures makes them essential in aerospace and power generation. However, the manufacturing processes for these alloys can be complex and require careful attention.
One popular method is arc melting. This technique uses high electrical currents to melt the alloys under a vacuum. It ensures a homogeneous mix of metals. However, slight variations can lead to inconsistencies in the final product. According to a recent industry report, arc melting has a production efficiency of around 80%. This highlights both its reliability and limitations.
Powder metallurgy is another effective method. It allows for precise control over the size and distribution of particles. The process involves pressing and sintering metal powders. A study showed that using this method can enhance mechanical properties, but it can also be costlier and time-consuming. Maintaining high quality in production remains a challenge. Even minor errors in the process can lead to significant performance issues in the final alloy.

High melting point alloys are gaining attention due to their unique properties. These materials can withstand extreme temperatures, making them valuable for various applications. Industries like aerospace and defense are particularly interested in these alloys. They offer excellent strength and durability when exposed to high heat. This ensures the safety and reliability of components in critical environments.
Future trends suggest that research will focus on improving the performance of these alloys. Scientists are exploring new compositions to enhance their thermal stability. They aim to create lighter alloys without compromising strength. This could lead to greater energy efficiency in engines and turbines. However, challenges remain. Standardization of testing and production methods is essential but often overlooked.
There is a push for sustainable practices in alloy production. Developing eco-friendly materials could mitigate environmental impacts. But, the recycling of high melting point alloys often poses difficulties. Many existing methods are not efficient. Addressing these reflections is crucial for future advancements. As innovation continues, the quest for optimal high melting point alloys will undoubtedly evolve.