In today's manufacturing landscape, the adoption of Powder Metals is transforming production methods. Experts highlight that these materials offer significant advantages. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading figure in materials science, noted, "Powder Metals enable unparalleled precision and customization in manufacturing." This statement resonates with many industries seeking efficiency.
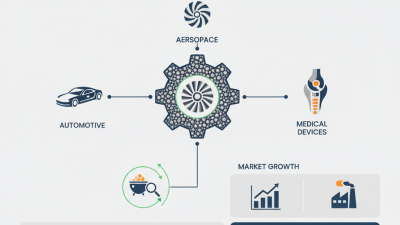
The benefits of Powder Metals extend beyond mere precision. They allow for the creation of complex geometries and reduce waste during the manufacturing process. For example, industries like aerospace utilize this technology to ensure lightweight yet sturdy components. Enhanced thermal properties are also a significant gain, as Powder Metal components often feature better heat resistance.
However, challenges accompany these benefits. The initial cost of equipment can be high. Additionally, not all manufacturers are familiar with the techniques required to handle Powder Metals. As industries evolve, educating teams on these materials becomes essential. Overall, the transition to Powder Metals requires careful consideration and adaptation to fully realize their potential.

Powder metals have become pivotal in modern manufacturing techniques, offering numerous advantages. Their unique properties allow for precise shapes and sizes, reducing waste significantly. This means manufacturers can produce high-quality components while conserving resources. The ability to create complex geometries is particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Tips: Always consider your material choice. Different powder metals yield various mechanical properties. Experimenting with blends may also provide better results tailored to specific applications.
The process of sintering transforms powder into robust parts. However, it requires careful temperature control. If not managed properly, defects can occur. Monitoring this stage consistently can save time and reduce production costs.
Another aspect to reflect on is the efficiency of production. Powder metallurgy can lead to shorter lead times. Yet, initial setup costs may be high. Evaluating your budget and long-term needs can guide better decisions.
| Benefit | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | Reduces waste by utilizing nearly 100% of the material. | Automotive, aerospace components |
| Complex Shapes | Allows for manufacturing of complex geometries not achievable with traditional methods. | Precision tooling, intricate parts |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower production costs due to efficient material usage and reduced machining. | Mass production |
| High Strength | Powder metals can achieve high density and strength through sintering. | Structural components |
| Custom Alloying | Ability to create specialized metal alloys tailored to application requirements. | Industry-specific applications |
| Rapid Prototyping | Speeds up the development process for new designs and components. | Product development |
| Reduced Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage compared to traditional metalworking processes. | Sustainability initiatives |
| Enhanced Properties | Allows for specific enhancements like improved wear resistance. | Tool and die manufacturing |
| Avoidance of Thermal Distortion | Minimizes thermal effects associated with traditional fabrication methods. | Precision applications |
| Improved Surface Finish | Higher quality surface finishes achievable compared to conventional methods. | Cosmetic parts, high-visibility items |
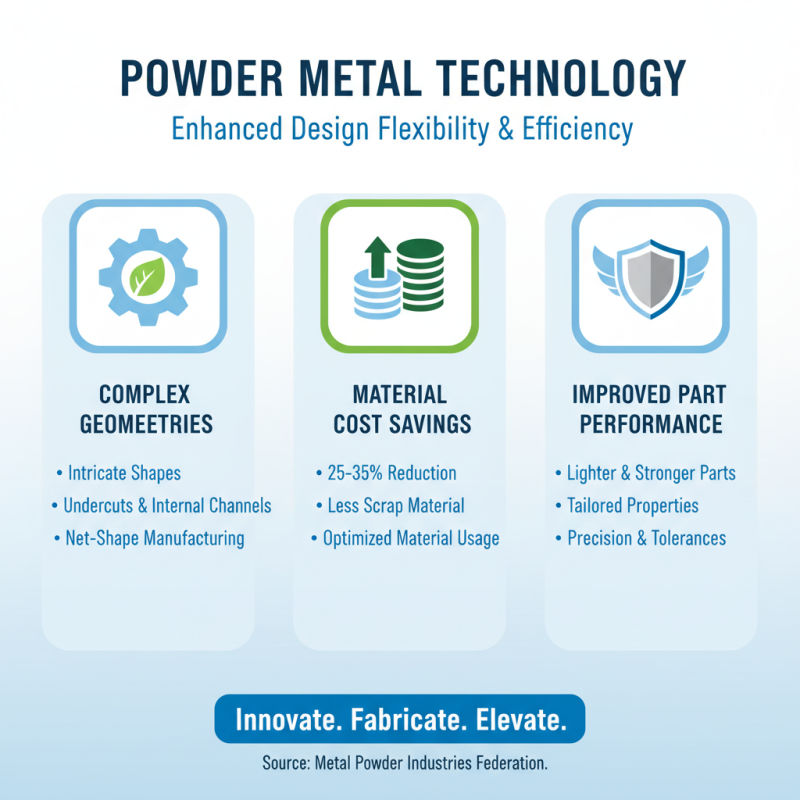
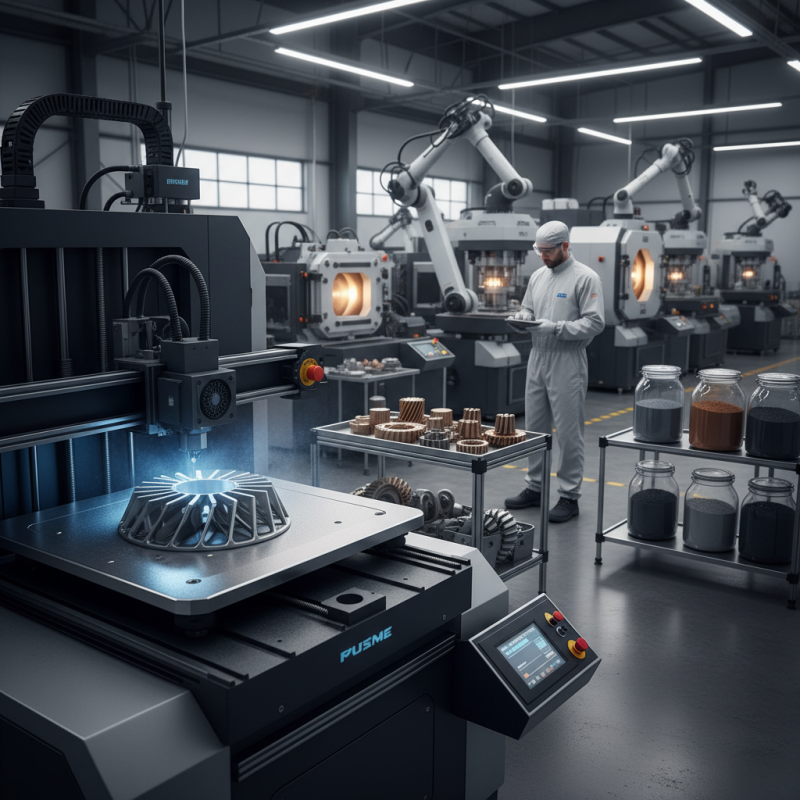
Powder metal technology offers enhanced design flexibility in modern manufacturing. This approach allows for complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. A report by the Metal Powder Industries Federation estimates that powder metallurgy can save up to 25-35% in material costs, illustrating its efficiency in design. With this method, manufacturers can create parts that are lighter and stronger, tapping into unique shapes that meet precise specifications.
The versatility of powder metals is a game-changer. Designers can explore intricate designs without compromising on structural integrity. Engineers can produce components that would be impossible using conventional machining methods. This freedom leads to innovative products and a collaborative environment between designers and manufacturers. It's important to evaluate your project's specific needs and how powder metals can align with them.
Tip: When designing with powder metals, consider the limitations and possibilities within each stage of production. Communication between teams is key. Be open to adjusting designs based on material behavior. Every decision impacts the final product and potential cost savings. Exploring new methods can reveal unexpected challenges and opportunities. Emphasizing flexibility in design can ultimately lead to more successful outcomes.
The use of powder metals in modern manufacturing has revolutionized production efficiency. It allows for intricate designs that traditional methods can't easily achieve. This precision reduces waste since parts can be made closer to their final shape. It can decrease material costs as less raw material is required overall.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant advantage of powder metallurgy. It minimizes the energy used during production, leading to lower operating costs. Manufacturing processes such as sintering are generally less energy-intensive than conventional methods.
However, the initial setup for powder metal production can be expensive. Companies might need to weigh the high upfront costs against long-term savings.
Another aspect is that not all materials are suited for powder metallurgy. Manufacturers should evaluate the properties of different metals during design. It's essential to recognize that while powder metals offer many advantages, they may not be the best solution for every application. Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for optimizing their use in production.
Powder metallurgy offers significant advantages in modern manufacturing. Its unique properties often outperform traditional methods. For instance, parts made from powder metals can achieve tighter tolerances. This precision enhances the overall performance of components used in automotive and aerospace applications.
A report by the Metal Powder Industries Federation indicates that powder metallurgy can produce components that are 30% lighter. This reduction is vital for industries aiming to improve fuel efficiency. The superior mechanical properties include strength, ductility, and resistance to wear. Materials like tungsten and titanium, commonly processed this way, showcase remarkable durability in extreme conditions.
However, the process isn't flawless. Some manufacturers face challenges in controlling the uniformity of powder particles. Variations in size can impact the final product's integrity. This inconsistency might lead to defects, questioning the reliability of certain applications. Therefore, refining the powder production process remains a critical focus in the industry.

Powder metals are gaining traction for their sustainability benefits in modern manufacturing. Research shows that these materials often require less energy during production compared to traditional methods. For instance, a report by the Metal Powder Industries Federation indicates that the energy consumption can be reduced by up to 30% when using powder metallurgy instead of conventional casting.
Moreover, powder metallurgy processes generate minimal waste. Unlike machining, which can lose up to 80% of raw material, powder processes can achieve near-net shapes. This efficiency directly translates to lower material costs and a reduced ecological footprint. The International Powder Metallurgy Association highlights that the recycling rate of powder metals can reach over 90%. This impressive statistic underscores the potential for sustainable practices in manufacturing.
While these benefits are significant, challenges exist. Not all powder metals are recyclable, and the processes aren’t universally applicable. Additionally, there is a need for increased awareness among manufacturers about sustainable practices. Investment in research and development is essential to overcome these limitations. As the industry evolves, so must the commitment to integrating sustainability into core practices.